Ambisonics is a way of representing a full-sphere sound field so you can capture, store, transmit, and later reconstruct it in different formats (headphones, speakers, VR environments, etc.).
Instead of recording sound channel-by-channel (like stereo’s L/R), Ambisonics encodes the sound field itself into a set of mathematical components — spherical harmonics — which describe how sound arrives from all directions.
Think of it as:
- Encoding: Turning “sound coming from this angle” into a math-based format that’s independent of playback setup.
- Decoding: Turning that math back into sound for a specific speaker arrangement or binaural headphone playback.
Ambisonic REAPER
This guide showcases how to create an Ambisonic REAPER composition that will spatialize sound inside the Immersive Arts Space.
- Download REAPER.
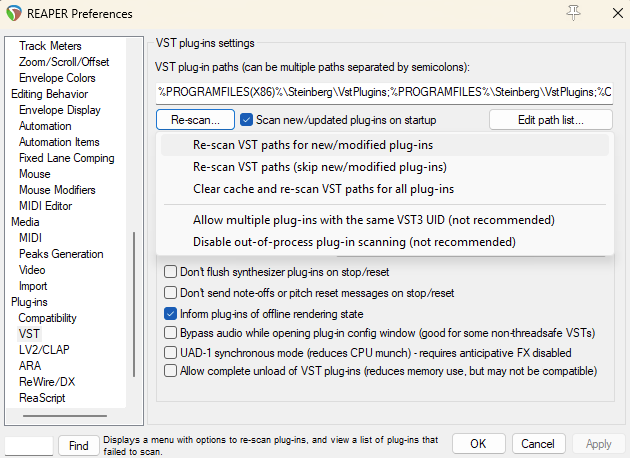
- Download Ambisonic for REAPER (it’s available for Mac and Windows ), and make sure it is imported in REAPER inside REAPER Preferences > VST by using the Re-Scan… > Re-scan VST path new/modified plug-ins.
Setup
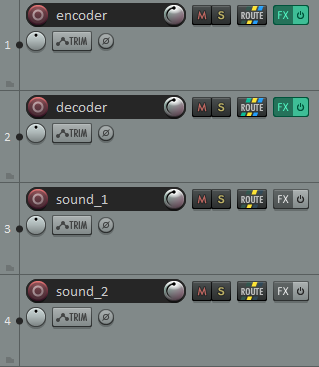
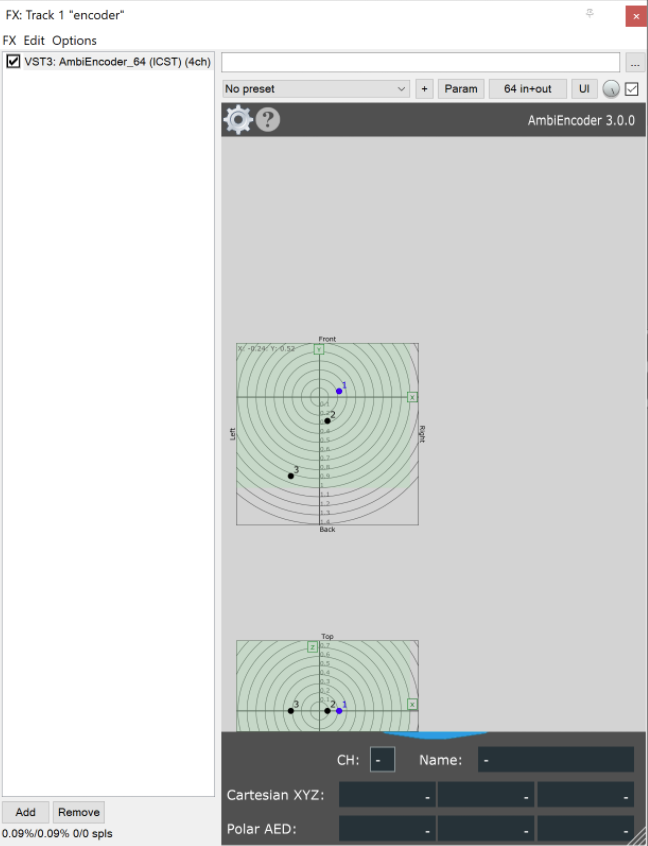
- In REAPER, add a new audio track called encoder, click the FX button and make sure to select VST3: AmbiEncoder_64 (ICST).
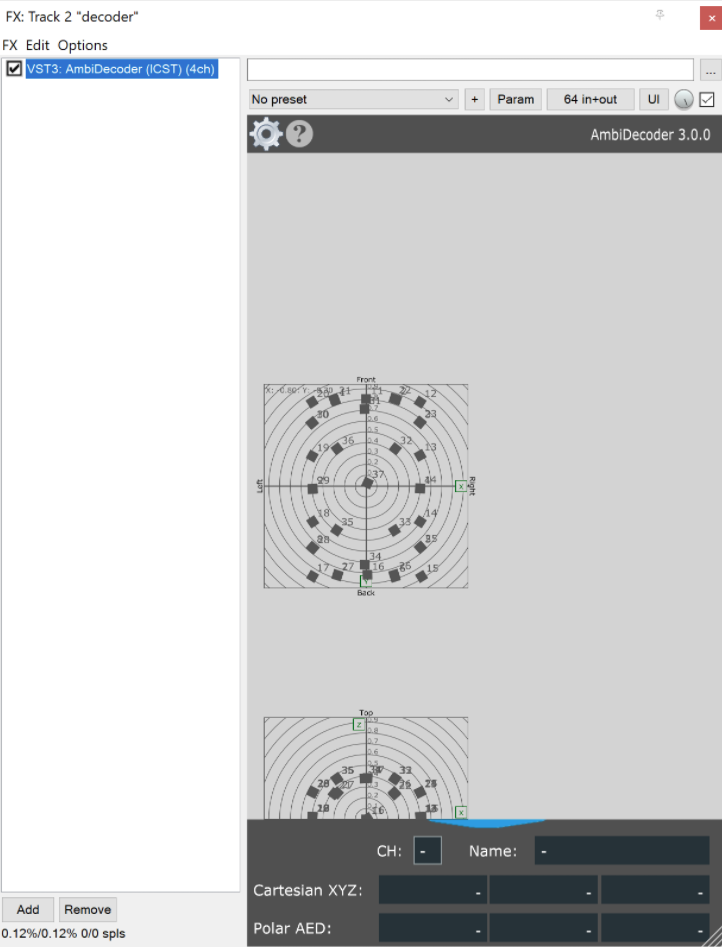
- Add a second audio track called decoder, click FX and make sure to select VST3: AmbiDecoder (ICST).
- Add additional audio tracks base on how many sound/tracks you wish to spatialize. Import and add your sound/composition in the sound_x track(s).
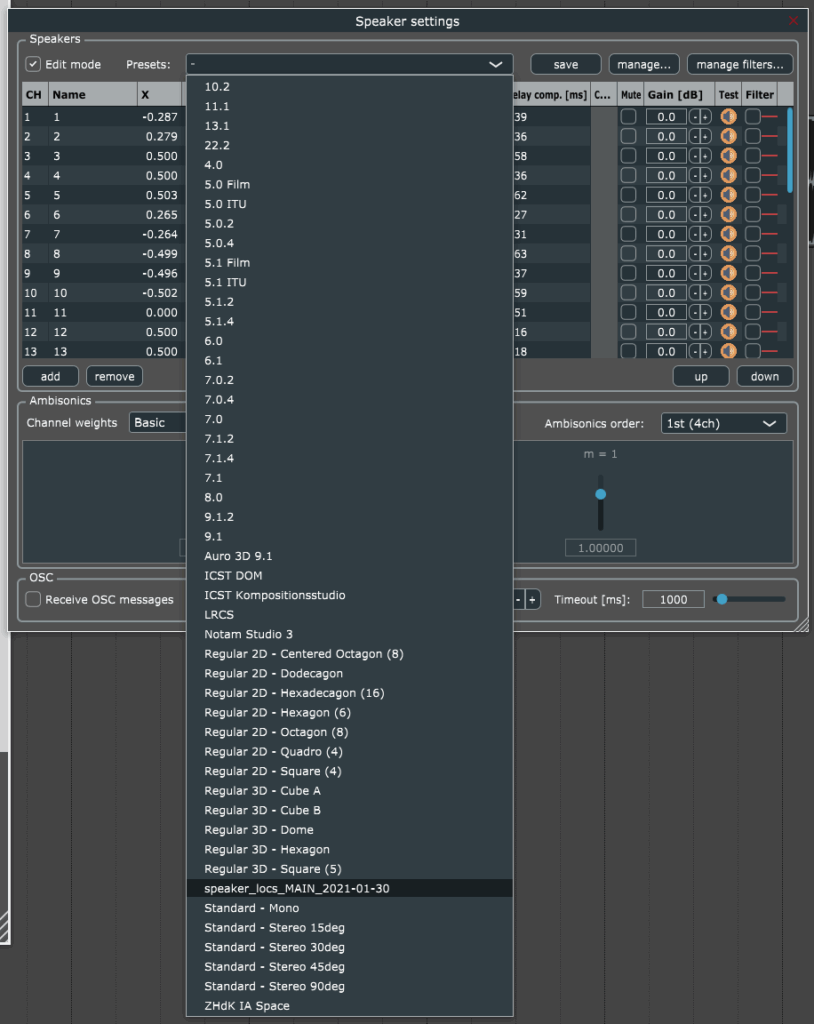
- Download the IAS speaker configuration (for 38 channels).
- Import the IAS speaker configuration in REAPER. To do so in the decoder track, click the FX button, then click on the ⚙ > manage… > import once the file is imported make sure to select the new preset and apply.
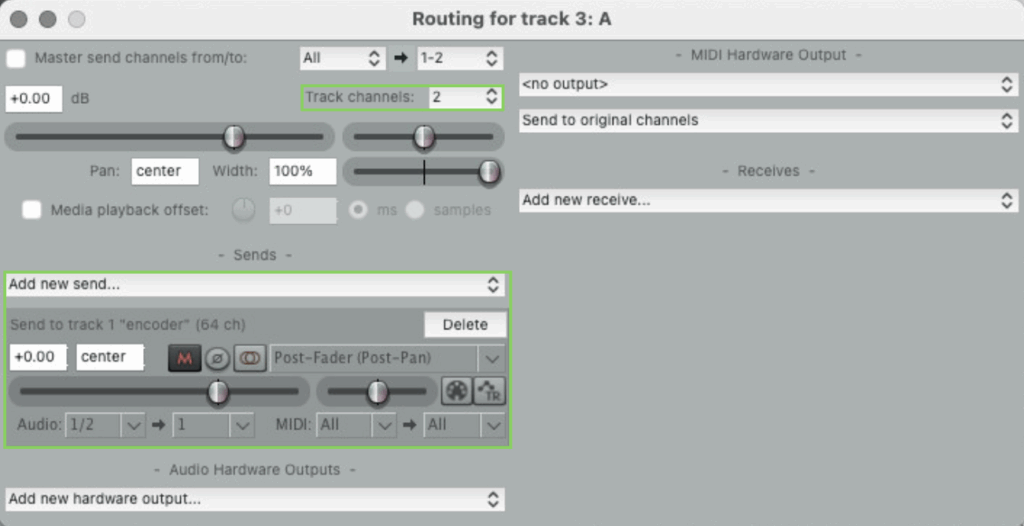
- Set the routing settings for the encoder, decoder and your sound tracks (on the keyboard press Ctrl+M to display the Route button). Follow the images below to configure each track.
Encoder routing settings
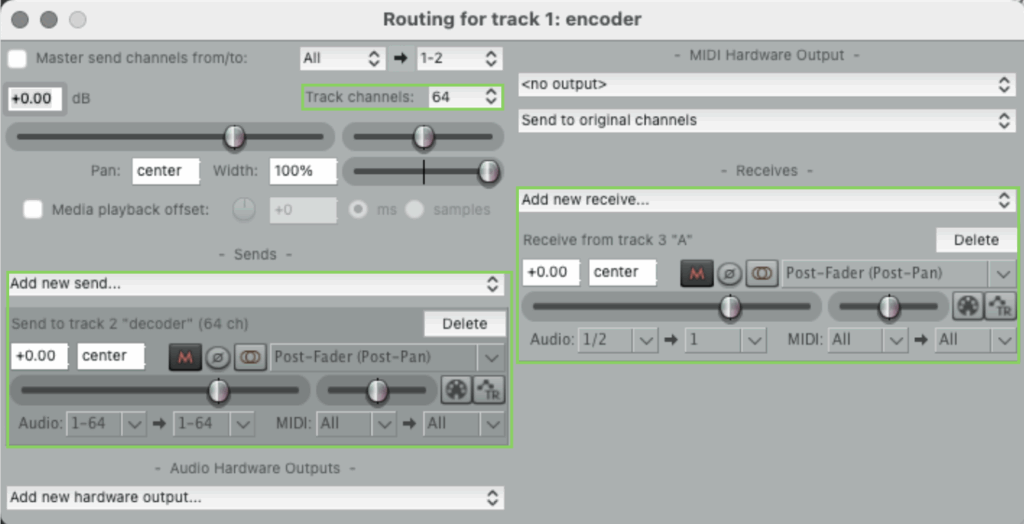
When we encode, we take the sound from a source (for example, in this case the sound_1 on track 3) and project it onto a set of spherical harmonic functions.
Decoder routing settings
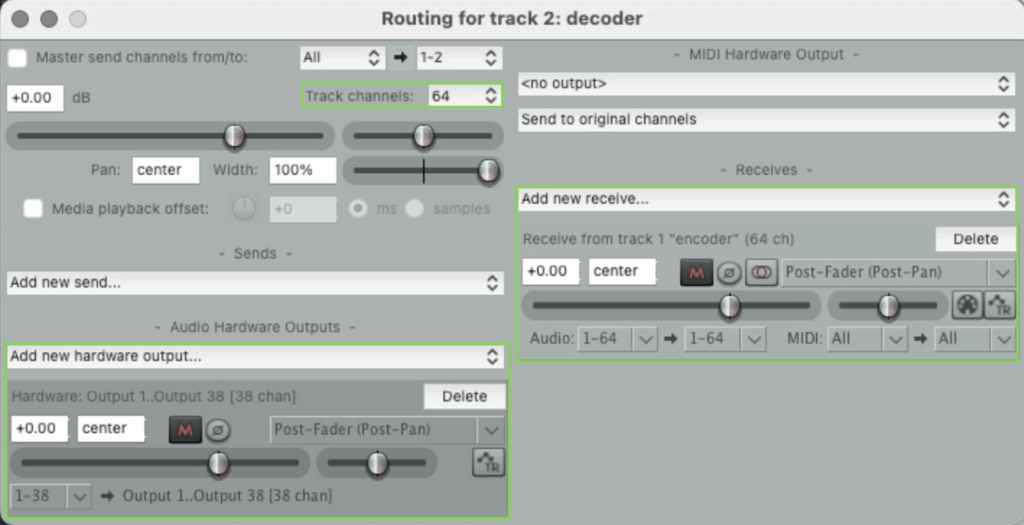
When decoding, we take the Ambisonic channels (W, X, Y, Z, plus higher-order ones if present) and remix them for speaker arrays (e.g., cube, dome, 360° setup) or binaural output (headphones, stereo setup). The decoder applies speaker direction vectors or HRTF filters to reconstruct the directional cues.
Sound(s) routing settings